Sideways Trend, as the name suggests, is sideways- absence of any clear directional bias in the market.
Such horizontal price movement occurs when the forces of supply and demand (of the underlying) are nearly equal. Generally, sideways trend is a period of consolidation before the price continues in the direction of the previous move. Sideways price action is also known as “horizontal trend”.
How a share trader can tackle sideways market
Moving on to today’s discussion: “how to tackle sideways markets”, there are two distinct trading philosophies:
- Buy low, sell high (for Sideways markets, i.e. MCX wheat prices right now)
- Buy high, sell higher (for trending markets, i.e. Indian stock indices right now)
So our trading strategy depends on the market conditions we are in. The real problem is to know “which market condition is prevailing?”
Importance of Entry Point
When market is trending, Mantra is “Trend is your friend”. Every price would eventually become a good price so long as you are with the trend. In such conditions we find even a layman claiming victory and making at least some money. However trouble starts when market loses its bias and conditions become “zig-zag”. Laymen loses calm while helplessly watching his position on both sides of the equator. It is in such an environment that, entry point becomes particularly important.
Also Read : Insider Trading: What It Means For You
Volumes
Falling volumes are typically associated with sideways market conditions. As the sideways conditions extend hedgers lose interest. On persistent sideways conditions, hedgers would start believing that this market doesn’t need hedging. Speculators also lose interest as they don’t get enough return to cover the cost of carrying positions. For speculators, managing such unproductive positions become fruitless efforts.
Open Interest
Slowly as market participants leave the market-place, open-interest also take a hit. Hence, sideways conditions are marked by falling volumes and open-interest.
Other way of saying the same would be, falling volumes and open-interest is an indication that trend is about to end. The end of the sideways market conditions is often preceded by increasing volumes and/or open interest.
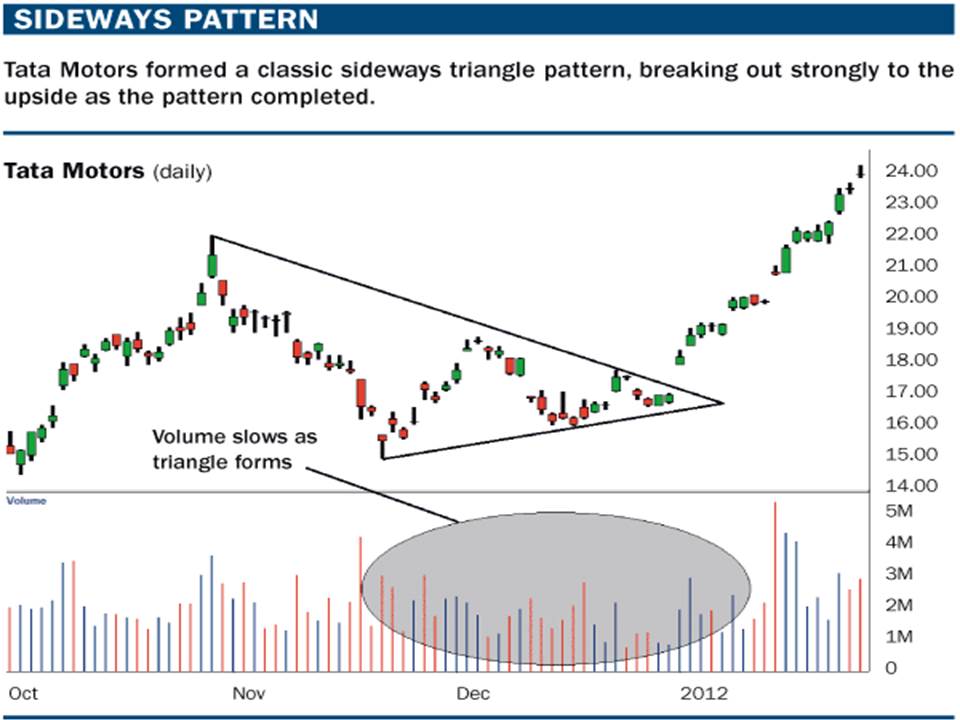
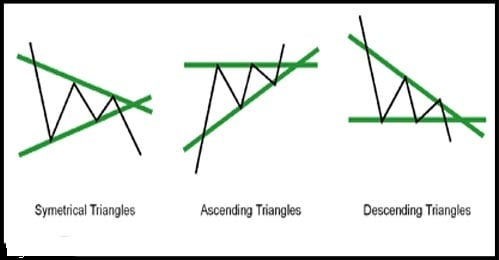
Technically speaking sideways conditions may form few set patterns. We would like to highlight here that identifying sideways patterns are the most difficult part of technical trading. Often price patterns can develop into more than a single set-up.
We suggest playing the probability game: attaching probability to all possible outcome and then trading based on most probable next move. Here are a few possible sideways technical set-ups:
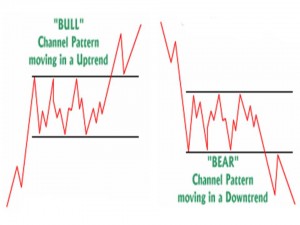
- Channel Patterns are indecision areas that usually break-out in the direction of the existing trend. The pattern does see some drop in volumes, as is normal for sideways conditions. But the drop in volumes was not as much as you would expect in other sideways patterns. Like the others sideways pattern, however, volumes should noticeably increase on the breakout to confirm the breakout.
o Target post breakout: On confirmed breakout, prices are expected to move as much as width of the rectangle from the breakout point.
o Stop for any such trade should be kept below the horizontal line which observed the breakout.
Also Read : India VIX Futures Trading
- Triangles are formed by drawing couple of trendlines connecting previous swing-lows and swing-highs. The lines get narrower over time because of lower tops and higher bottoms (unlike in channel).
o Target on break out is equal to the vertical distance at the start of the triangle, and is measured from the breakout point.
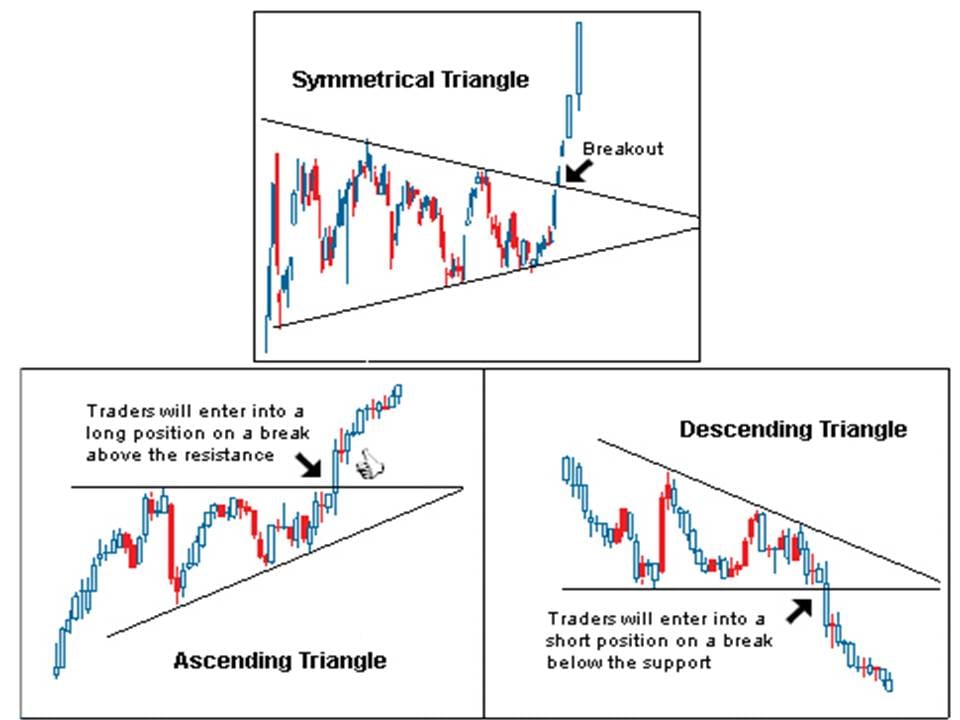
- Triple Tops and Bottoms are formed when the price movement tests a level of support or resistance three times and is unable to break through; this signals a reversal of the prior trend.
- Wedges are triangle look-a-like pattern but with “lower highs and lower lows”. The pattern normally sees breakout in the direction of the trend.
So these are some ways of tackling Sideways Market.
Open Lowest Brokerage Trading Account Here
[email-subscribers namefield=”NO” desc=”Subscribe now to get latest updates!” group=”Public”]