
If you are starting with options trading, you will frequently come across the terms call and put options. Understanding these terms and the differences between them is vital for success in options trading.
This article dives into the core difference between these two options, providing a clear understanding of what each entails and when they might be used. We’ll also see some of the potential risks involved in both and how to mitigate them. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting to explore options trading, this guide will help you hone your investment strategies.
What Are Options?
Options are financial contracts that give you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a specific price by a certain date. Think of them as a permission slip with an expiration date.
Imagine you see a concert ticket going for ₹100 (Indian Rupees), but you’re not sure if you can attend. An options contract lets you secure the option to buy the right to that ticket for ₹100 (the strike price) by a specific date (expiration date). Think of it as a down payment to hold that price for you on the underlying asset (the concert ticket). You’re not obligated to buy the ticket, but you have the right to if the price goes up or you decide you want to go. This can be useful if you think the price of the ticket might go up in the future, but you’re not sure yet.
Options contracts are used for a variety of investments, not just concert tickets, but the concept remains the same: you’re buying the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell something at a specific price by a certain date. In the world of finance, options work similarly, but instead of concert tickets, they deal with assets like stocks, bonds, or currencies.
Now that we have a better understanding of options, let us look further into the 2 types – call options and put options.
What Is a Call Option?
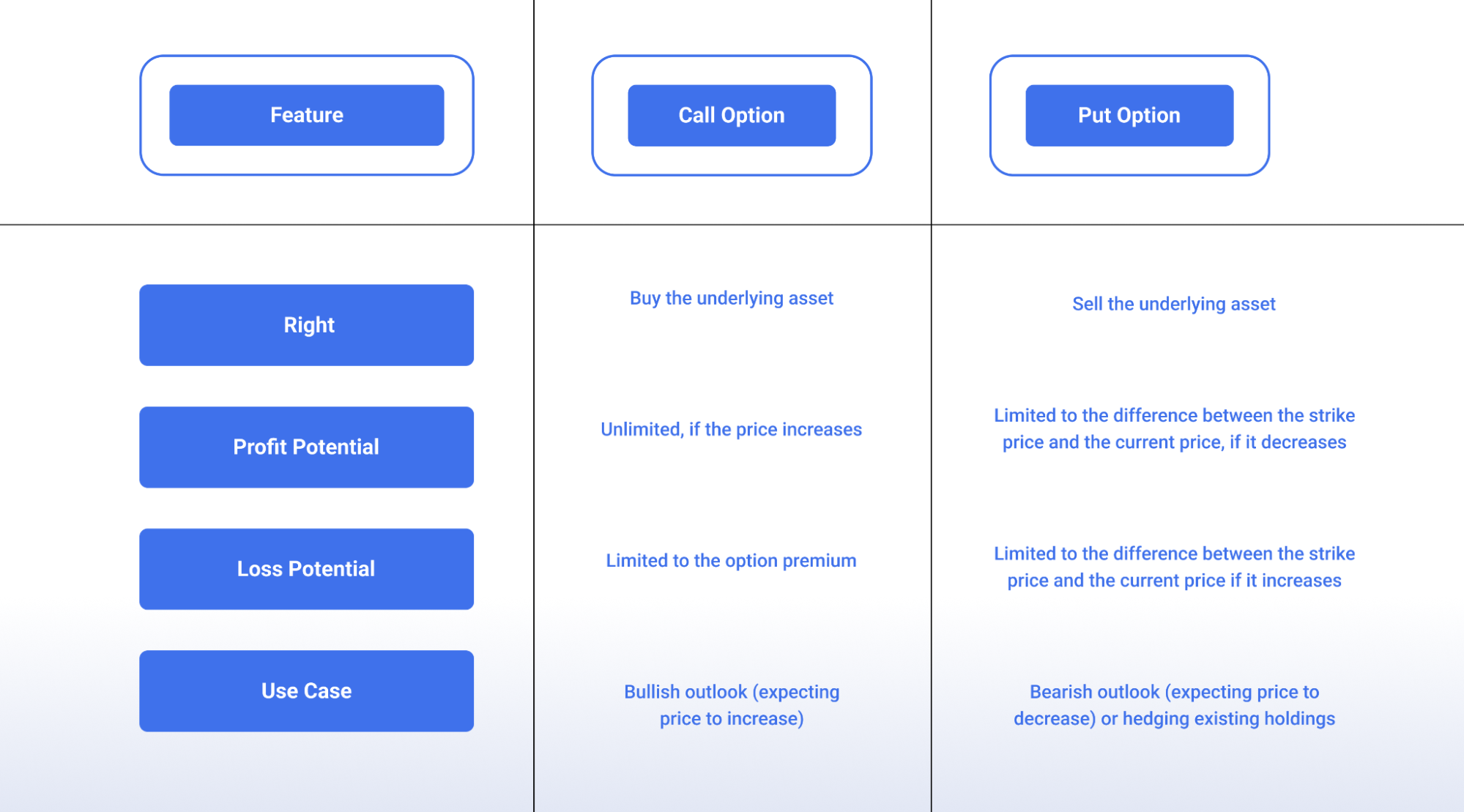
A call option is a financial contract that gives the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to buy (or call) a specific asset, like a stock, at a predetermined price (strike price) by a certain date (expiration date). It’s like having a contract that guarantees you the chance to purchase something at a set price, regardless of the market price, within a specific timeframe.
The key features of a call option include:
- Right to Buy: You have the right, but not the compulsion, to buy the underlying asset.
- Predetermined Price (Strike Price): This is the specific price you can buy the asset at if you exercise the option.
- Specific Date (Expiration Date): This is the deadline by which you must decide whether to buy the asset or let the option expire.
Imagine you believe a stock’s price will increase in the future. By buying a call option, you secure the right to purchase that stock at a specific price (strike price) even if the market price goes higher. You only pay a premium (a fee) for the option, not the full price of the stock upfront. If the stock price goes up as you expected, you can exercise the option to buy the stock at the lower strike price and potentially make a profit. However, if the stock price goes down, you can simply let the option expire and lose only the premium you paid.
What is a Put Option?
A put option is a financial contract that grants the buyer the right, but not the obligation, to sell a specific asset, like a stock, at a predetermined price (strike price) by a certain date (expiration date). Think of it as an insurance policy for your holdings or a way to profit from a price decline.
The key features of a put option include:
- Right to Sell: You have the right, but not the requirement, to sell the underlying asset at the strike price.
- Predetermined Price (Strike Price): This is the specific price at which you can sell the asset if you exercise the option.
- Specific Date (Expiration Date): This is the deadline by which you must decide whether to sell the asset or let the option expire.
Imagine you own a stock and you’re worried about a potential price drop. By buying a put option, you secure the right to sell the stock at a specific price (strike price) even if the market price goes down. You pay a premium for this right, but it acts like a safety net. If the stock price falls, you can exercise the option to sell your shares at the higher strike price, potentially limiting your losses. However, if the stock price goes up, you can let the option expire and lose only the premium.
Difference Between Call Option and Put Option
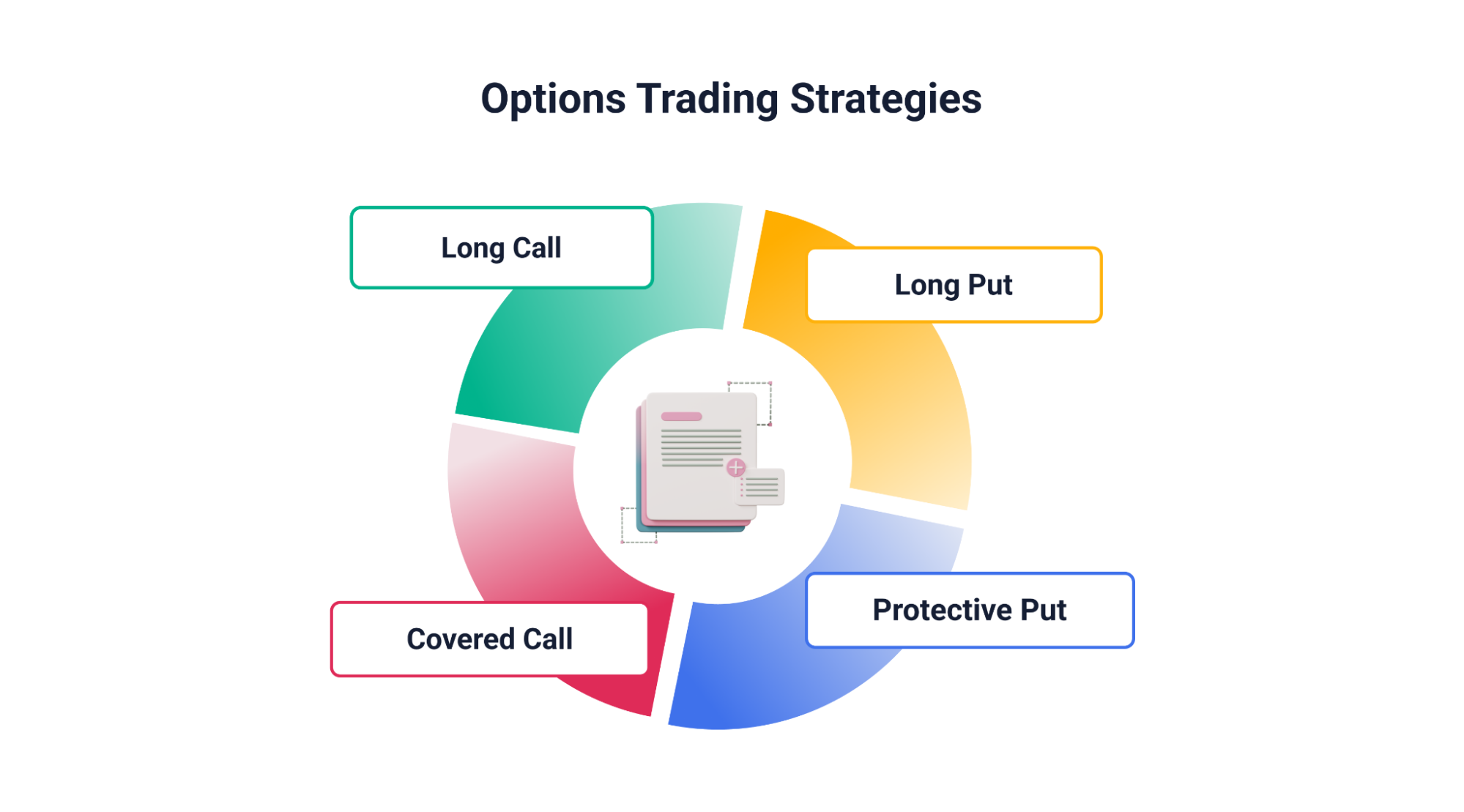
Understanding Option Trading Strategies
Stock options can be leveraged by investors to gain profits, but it also comes with complexities. Unlike simply buying or selling a stock, options offer a wider range of strategies to potentially profit from market movements, hedge existing holdings, or generate income.
Let’s take a look at some call and put options trading strategies –
1. Long Call
This is the most straightforward strategy. You buy a call option because you believe the price of the underlying asset will rise above the strike price by expiration. If your prediction is correct, you can exercise the option and purchase the asset at the lower strike price. The profit arises from the difference between the strike price and the higher market price.
2. Long Put
This strategy is used when you believe the price of the underlying asset will fall. You buy a put option, giving you the right to sell the asset at the strike price by expiration. If the price drops, you can exercise the option and sell the asset at the higher strike price, limiting your losses.
3. Covered Call
This is a more conservative strategy for stock owners who want to generate income while still holding the stock. You sell a call option on a stock you already own. If the stock price rises above the strike price by expiration, the buyer will exercise the option, and you will be obligated to sell your shares at the strike price. You collect the premium upfront as compensation for potentially selling your stock at a predetermined price.
4. Protective Put
This strategy is used to hedge existing stock holdings against a potential price decline. You buy a put option on a stock you already own. If the stock price falls, you can exercise the put option to sell your shares at the strike price, limiting your losses.
As you gain experience, you can explore more intricate strategies involving combinations of options. These often involve buying and selling calls and puts simultaneously to create specific risk-reward profiles. Some popular spread strategies include:
- Bull Call Spread: A strategy for a moderately bullish outlook, limiting potential profit but also reducing risk compared to a long call.
- Bear Put Spread: A strategy for a bearish outlook, limiting potential loss but also reducing profit compared to a long put.
- Straddle and Strangle: Strategies that profit from significant price movements in either direction, up or down.
Risks in Call and Put Options
While options offer exciting possibilities for magnified returns, they also come with inherent risks. Here’s a breakdown of the key risks associated with each:
Call Option Risks
Time Decay (Theta)
The value of a call option diminishes as time passes towards its expiration date. This is because the intrinsic value (difference between the strike price and current asset price) erodes, leaving only time value (potential for future price increase). If the underlying asset price doesn’t rise significantly before expiration, the option can become worthless, resulting in a loss of the entire premium paid.
Unlimited Loss Potential
Unlike the limited risk of buying a stock (your maximum loss is the purchase price), call options have the potential for unlimited losses. If the price of the underlying asset falls significantly, the call option becomes worthless, but you still lose the premium you paid.
Market Direction
Call options are for bullish bets. If the market moves sideways or even dips slightly, the call option might expire worthless, leading to a loss of the premium.
Put Option Risks
Time Decay (Theta)
Similar to call options, put options also suffer from time decay. As expiration approaches, the time value diminishes, and if the underlying asset price doesn’t fall as anticipated, the put option can expire worthless, resulting in a loss of the premium paid.
Limited Profit Potential
Unlike call options with unlimited profit potential, put options have limited profit potential. The maximum profit is capped at the difference between the strike price and the purchase price of the asset, minus the option premium.
Increased Volatility
Put options can be riskier in highly volatile markets. If the price of the underlying asset swings wildly, the put option might become more expensive due to increased volatility, even if the overall trend isn’t necessarily downwards.
Some additional risks to keep into consideration about options trading are –
Margin Requirements
Selling uncovered call options (selling a call option without owning the underlying asset) or naked puts (selling a put option without holding the underlying asset or cash to buy it) involves margin requirements. This means you’ll need to tie up a certain amount of capital to cover potential losses, which can magnify risks.
Complexity
Options trading strategies can get a bit complicated, especially when combining calls and puts. It’s crucial to understand the mechanics of each strategy and its risk profile before deploying it with real capital.
How to Mitigate Options Risks
One of the key ways to mitigate risks is to begin with well-defined strategies like long calls or long puts before venturing into complex spreads.
By understanding these risks and employing sound risk management techniques, you can navigate the world of options trading with a more informed and measured approach. Remember, options are powerful tools, but they require careful consideration and a healthy respect for the inherent risks involved.
Conclusion
Options trading enables investors and traders to get more returns on top of regular securities (stocks, bonds, etc.) trading and investing. However, it is crucial to understand the concept before starting to practice it in the real world. By familiarizing yourself with call and put options, their core functionalities, and the strategies they enable, you can craft a more dynamic investment approach.
Remember, options trading comes with inherent risks. It is necessary to prioritize sound risk management and start with basic strategies before venturing into complex ones. With a measured approach and a thorough understanding of the risks and rewards, options can add a new dimension to your investment journey.
Want to explore options trading? TradeSmart can help you make sound trading decisions with over 2 decades of experience in stocks. Start your journey by opening a FREE demat account with us and trade with a brokerage rate of only ₹15 per executed order.
Disclaimer: This article is for information purposes only and should not be considered as stock recommendation or advice to buy or sell shares of any company. Investing in the stock market can be risky. It is therefore advisable to research well or consult an investment advisor before investing in shares, derivatives or any other such financial instruments traded on the exchanges.
FAQs
Q. What are the main differences between call and put options?
Call options allow buying at a predetermined price in bullish markets, while put options enable selling at a set price in bearish scenarios.
Q. How do options trading strategies vary based on market outlook?
Long calls profit from price increases, long puts from decreases, covered calls generate income in neutral markets, and protective puts shield against losses.
Q. What are the risks associated with call options?
Risks include time decay (options’ value reduces over time), potentially unlimited losses, and the possibility of expiring worthless if the market moves unfavorably.
Q. How do put options protect investors in volatile markets?
Put options provide a safeguard against losses by allowing selling at a predetermined price, but can become more expensive in volatile markets.
Q. How can investors mitigate risks when trading options?
Mitigation involves starting with basic strategies, aligning expiration dates with market outlooks, selecting options with low implied volatility, and implementing proper risk management techniques like stop-loss orders.











[…] Call vs Put Option – It is important for you to know the difference between Call and Put Option if you deal in Futures and Options. Read the complete article to know in detail at TradeSmart. […]