Introduction
Technology advancement has changed many sectors over the last two decades and has acted as a disruptor on many occasions across the globe. One sector that has seen a sea change through the advent of technology has been broking in the financial sector, which has given a boom to the practice of online trading among beginners.
Technology has not only brought transparency in the sector but also helped increase the reach to clients across the country and bring down the cost considerably. This has been possible through online broking where the clients themselves punch in their buy and sell orders using internet-based platforms using their computers or mobile without calling their brokers for every execution.
Given the low rates and ease of doing business, it is not shocking that market share online brokers now account for the lion’s share of the retail broking market.
To get a deeper insight into online broking, here is an Online Stock Trading Beginner’s Guide on the subject covering various aspects of the industry.
What is Online Trading?
Trading involves making predictions about whether the price of a financial asset will increase or decrease without actually owning the asset. It involves speculating on market price movements across various financial markets, such as stocks, forex, commodities, indices, and bonds. Online trading is the process of buying and selling financial securities, such as stocks, bonds, currencies, and commodities, through internet-based platforms provided by brokerage firms. It allows investors to execute trades electronically from anywhere with an internet connection. This method of trading provides convenience, cost-effectiveness, and direct control over trading decisions to investors, enabling them to access a wide range of financial markets and instruments quickly and efficiently.
How Can You Start Online Trading as a Beginner?
It is often daunting for beginners to actually break into the trading world, to ease up the process, one can follow the steps mentioned below in the given order:
1. Selecting an Online Broker
Online brokers offer lower brokerages than offline brokers. However, not all online brokers are the same. In order to pick up an online broker, one needs to look at other factors apart from the brokerage rates.
The trading platform that the broker uses will decide the ease of entering and exiting orders and also the speed. A broker with a strong trade engine is to be preferred. A social media scan or reviews can be used to determine which broker offers a strong trading platform. A client should prefer a broker with a robust trading platform.
These days many brokers are offering charting facilities with their broking account. A trader can not only view chart prices but also can directly trade from the charts. This feature has eased trading further.
Offline service issues and grievance handling in case a trading terminal not functioning properly also needs to be considered while selecting an online broker.
The ease of transferring money in and out of the broking account is an important feature that needs consideration. Timely payment into one’s bank account after a share should also be taken into account and can be validated by social media posts and comments plus checking on neutral finance sites.
Finally, one should check that the broker is registered with the market regulator SEBI and is a registered member of all major stock exchanges in the country.
2. Opening a Trading Account
Most brokers these days have streamlined their account opening process. Account openings are done through an online process which requires submission of details and documents through the internet. This move has helped cut down account opening time and in many cases, it has been done within hours.
While opening an account one needs to be clear on which segments he is interested in or would like to trade in future. Suppose a person is only interested in trading in equities, that too in the cash segment, there is no need for him to open an account in the derivative, commodity or currency segment.
If the person would like to start with the cash segment initially and later migrate to other segments, it is better to mark all the segments in the first instance itself.
The documents required for opening an online broking account are normally standard but may vary a bit from broker to broker. The standard documents required are PAN Card, Aadhaar Card, address proof, a mobile number linked to Aadhaar Card, bank statement, a cancelled cheque leaf and a photograph.
3. Opening of a Demat Account
Along with the trading account, a client also needs to open a Demat account from where his shares will be credited and debited as he or she trades.
While a client can have a Demat account with another broker or a bank it is advisable to have the trading and Demat account at the same broker to enable smooth functioning and saves everyone the time and hassle. Further, it also helps protect a client from the occasional auctioning of his shares in case he forgets transferring it or is unable to do so for various reasons.
Demat accounts are online and a client can easily access his account to see the shares that are in them.
4. Selecting a Suitable Brokerage Plan
Online brokers offer various types of brokerage plans to meet the requirements of different types of clients. Depending on the volume or frequency of trade one can choose from the different types of brokerage plans available.
The most common types of brokerage plans in the industry are fixed brokerages, monthly brokerage plans, and unlimited brokerage plans among others. Brokerage plans will differ from broker to broker and the client needs to compare them carefully. Many brokerages also allow a client to shift from one plan to another trading account.
Brokerage rates are different in all segments of the market – cash, derivative, forex and commodities. Also, tax and other charges will differ in all of these segments and will be charged at actuals as laid down by the authorities concerned.
5. Calculating Brokerage
Many brokers or finance sites have a brokerage calculator which helps the client to see how much brokerage will be deducted for the transaction he does. One needs to remember that these calculators will be taking into account the tax and other mandatory charges suggested by the Ministry of Finance, market regulator SEBI and stock exchanges at the actual rates. These rates will remain constant across all brokers.
6. Signing up for an Online Stock Trading App
Most brokers that offer online trading facilities also have a mobile app. The same account used for online broking can be used in this app. Both accounts are always mapped and will show the same information.
Suppose a trade is taken on an online platform and the trader has to go away from his computer, he can square off or view the same trade using his mobile app. One needs to remember that the same login should be used for both platforms.
7. Figuring Out Margins
Margin is the amount a client has to keep with the broker based on which the limit is assigned for trading. Margins can be in the form of cash or other forms of deposits like shares or fixed deposits among others. While cash and shares are the common forms of margins many brokers allow different financial assets also as margins. One needs to check with the broker before opening an account as to which mortgages are allowed with them as margins. Brokers use margins as a tool to attract customers. Aggressive brokers use very high margins to attract clients.
8. Analysing a Stock
Gain a solid understanding of both fundamental and technical aspects of stocks to strategize your trading approach. Fundamental analysis involves assessing a security’s intrinsic value by examining factors like earnings, expenses, and assets versus liabilities. On the other hand, technical analysis relies on past price and volume data to forecast the future potential of a stock. It is crucial to have some research done from your end, which you can further supplement with the available information and make a sound decision while picking a stock.
9. Learning to Stop Loss & Playing Safe
Volatility is an inherent aspect of the stock market, making it crucial for beginners to learn how to mitigate potential losses. Implementing a stop-loss strategy when executing trades is essential to minimise losses, as failure to do so can significantly impact your capital and dent your confidence, especially early on. Opting for less volatile stocks initially can provide a more stable starting point, albeit with slower progress. Opening a demat account and gaining comprehensive knowledge of the stock market are essential steps to navigate market volatility effectively and improve your chances of success.
Types of Capital Markets
The primary market and secondary market represent two essential components of the capital market, each playing a distinct role in facilitating investment activity and capital formation. Understanding the differences between these markets is crucial for investors and market participants alike, as they navigate the complexities of buying and selling securities.
1. Primary Market
The primary market is the initial point of sale for newly issued securities, where companies or governments raise capital by selling stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments directly to investors. In this market, companies undergo processes such as initial public offerings (IPOs) or bond issuances to raise funds for various purposes, such as expansion, research and development, or debt refinancing. Investors purchase these securities directly from the issuing entity, and the proceeds from the sale go to the issuer. The primary market plays a crucial role in facilitating capital formation and enabling companies to access funding for growth and development initiatives.
2. Secondary Market
The secondary market, unlike the primary market, is where previously issued securities are traded among investors. It is characterized by the buying and selling of securities that have already been issued and initially sold in the primary market. In the secondary market, investors trade securities among themselves without the involvement of the issuing company. This market provides liquidity to investors, allowing them to easily buy and sell securities based on prevailing market conditions and investor sentiment. Secondary market transactions do not generate funds for the issuing company; instead, they enable investors to adjust their investment portfolios and capitalize on market opportunities.
Types of Online Trading
There are different types of securities pertaining to different investment goals and the risk appetite of individual investors. It is important to figure out your specific requirements and then go ahead with online trading. Some types of securities which are traded online and trading practices are listed below:
1. Online Share Trading
Online share trading means buying and selling shares in the cash market. A trader can buy and sell shares in this market segment either with the purpose of selling his shares the same day which is called intra-day trading or can carry it forward and take delivery of the same, which can be for a few days to years. He or she will have to specify what type of trade will be taken at the time of the transaction. All intra-day orders have to be squared off by the end of the day. If the client does not do so, most brokers automatically square off all orders marked as intraday a few minutes before the closing bell.
This timing of compulsory square-off also varies with brokers. Some brokers also charge a fee if the transaction is compulsorily squared off. Short-sell that is selling of shares without actually having them, is allowed only in the intraday segment. All buy orders can be changed from intra-day to delivery provided there is enough cash in the client’s account to take delivery but sell orders cannot unless the client has those shares in their Demat account.
There are different order types which also change with brokers. One needs to understand the different types of orders the brokers offer before starting trading. There are different nomenclature for intra-day and delivery trading with brokers. Plus there are stop-loss orders and limit orders which need to be understood before taking a trade.
2. Online Trading in Derivatives
Online trading is also allowed in futures and options segments. While the trading methodology remains more or less the same in the cash as well as derivative segments, what changes are the margin system.
In this segment too, a position needs to be marked as intra-day or carry-forward while initiating a trade. Both the segments carry different margins which will again vary with the broker. A client should be clear on what margin norms the broker offers before opening the trading account. SEBI now has strict margin norms which have helped standardise the margin system across brokerages for delivery. However, brokers still have legroom where intraday is concerned.
3. Online Forex and Commodity Trading
Many online brokers also offer Forex and Commodity trading platforms on the same trading platform. Since shares, forex and commodities are all traded in different exchanges, a client needs to make sure that the broker they have selected is a member of all the exchanges.
Forex and Commodities trading operates in the same way as derivative trading. The Margin system for trading in these segments is different as compared to derivative trading and also differs from broker to broker.
Money transfer between various segments – shares, derivatives, forex and commodities is seamless and the client need not worry about transferring money from one segment to the other before trading. A trader can opt to trade only in forex or commodities without opening an account in the shares or derivatives segment.
How to Ensure Safety While Trading Online?
As online trading continues to grow in popularity, ensuring safety and security is crucial for investors. With the convenience of trading from the comfort of one’s home comes the responsibility of safeguarding personal and financial information against potential threats. One should keep in mind the following points to ensure safe online trading:
1. Choose a Reputable Brokerage Firm
Selecting a trusted and regulated online brokerage firm is the first step in ensuring safe online trading. Research reputable brokers that adhere to stringent security protocols and are registered with regulatory authorities.
2. Verify Website Security
Before entering any sensitive information or making transactions, ensure that the brokerage’s website is secure. Look for HTTPS encryption in the website address and a padlock icon in the browser bar, indicating a secure connection.
3. Use Strong Passwords
Create strong and unique passwords for your trading accounts, incorporating a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable passwords and refrain from sharing them with anyone.
4. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Enhance the security of your trading accounts by enabling two-factor authentication. This additional layer of security requires a secondary verification method, such as a code sent to your mobile device, to access your account.
5. Keep Software Updated
Regularly update your computer’s operating system, antivirus software, and trading platform to patch vulnerabilities and protect against malware, viruses, and cyberattacks.
6. Monitor Account Activity
Regularly monitor your trading account activity for any unauthorized transactions or suspicious activity. Report any discrepancies to your brokerage firm immediately and take the necessary steps to secure your account.
7. Educate Yourself
Stay informed about common online trading scams and fraud tactics to recognize warning signs and avoid falling victim to fraudulent schemes. Invest in financial literacy and educate yourself on best practices for safe online trading.
By following these pointers and adopting a proactive approach to online security, investors can minimize risks and safeguard their assets while engaging in online trading. Remember, vigilance and caution are essential in protecting against potential threats in the online trading world.
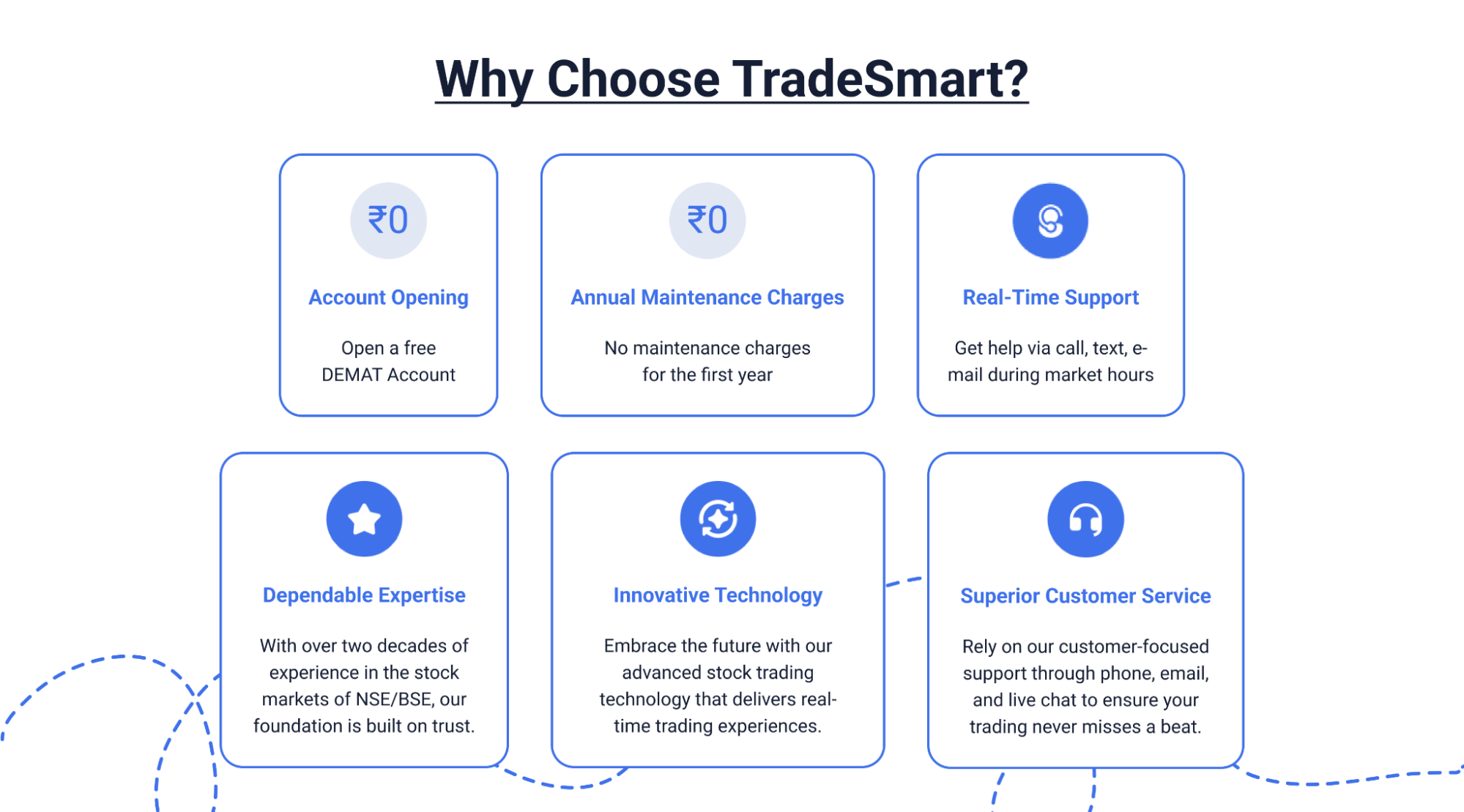
Why Choose TradeSmart?
Open a trading account with us and enjoy low ₹15 brokerage fees per executed order, no matter the trade size or market segment. We also offer leverage of up to 5 times on your equity trades, giving you more buying power for intraday opportunities. Need margin for your existing shares? We’ve got you covered. Plus, there’s no minimum commitment required to open an account, so you can try us out at your own pace.
FAQs
1. How can I start online trading for beginners?
To start online trading as a beginner, you’ll need to follow a few key steps. Firstly, select a reputable online broker that suits your needs and offers a user-friendly trading platform. Next, open a trading and Demat account online, providing necessary documents like PAN Card, Aadhar Card, and address proof. Once your account is set up, familiarize yourself with the trading platform and begin with small investments while gaining experience and knowledge about the market.
2. What is the best trading method for beginners?
For beginners, a straightforward approach is often the best. Consider starting with long-term investing in well-established companies rather than short-term trading. This involves buying and holding onto stocks for an extended period, benefiting from their growth over time. Additionally, practicing risk management strategies, such as setting stop-loss orders and diversifying your portfolio, can help mitigate potential losses.
3. How to select a brokerage plan?
When selecting a brokerage plan, consider factors such as brokerage rates, trading platform quality, customer service, and ease of fund transfers. Look for a plan that aligns with your trading frequency, investment goals, and risk tolerance. Compare different brokerage plans offered by reputable brokers and choose the one that best suits your needs and preferences.
4. What are the types of online trading?
Online trading encompasses various types, including:
– Share Trading: Buying and selling stocks in the cash market, either for intraday trading or delivery.
– Derivatives Trading: Trading futures and options contracts, with different margin requirements compared to share trading.
– Forex and Commodity Trading: Trading in foreign exchange and commodity markets, which operate similarly to derivative trading but with different margin systems and asset classes.
Choose the type of trading that aligns with your investment goals and risk appetite, and ensure the broker you select supports the desired trading segments.